Aws Kms Unable To Generate Data Key
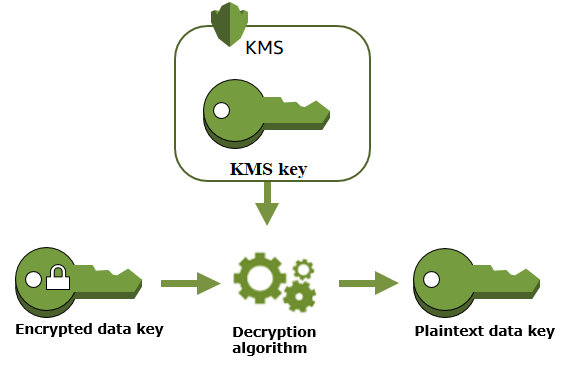
Now the developer wants to create the same encrypted database in the us-east-1 Region. Which approach should the developer take to accomplish this task? A) Create a snapshot of the database in the us-west-1 Region. Copy the snapshot to the us-east-1 Region and specify a KMS key. The examples in this topic use the Encrypt, Decrypt, and ReEncrypt operations in the AWS KMS API. These operations are designed to encrypt and decrypt data keys.They use an AWS KMS customer master key (CMK) in the encryption operations and they cannot accept more than 4 KB (4096 bytes) of data. Before storing the data, Slack checks its key cache for a suitable data key and, if none is found, generates one using the KMS GenerateDataKey API, using the permission granted by the key policy associated with that key. AWS KMS uses the CMK to generate a data key and returns a plaintext copy and encrypted copy to Slack.
With the release of version 2019.3, Tableau Server includes an updated key management system (KMS).
Tableau Server local KMS
The Tableau Server local KMS uses the secret storage capability described in Manage Server Secrets to encrypt and store the master extract key. In this scenario, the Java keystore serves as the root of the key hierarchy. The Java keystore is installed with Tableau Server. Access to the master key is managed by native file system authorization mechanisms by the operating system. In the default configuration, the Tableau Server local KMS is used for encrypted extracts. The key hierarchy for local KMS and encrypted extracts is illustrated here:
AWS KMS for encryption at rest
If your organization is deploying Data Extract Encryption at Rest, then you may optionally configure Tableau Server to use AWS as the KMS for extract encryption. To enable AWS KMS, you must deploy Tableau Server in AWS EC2. In the AWS scenario, Tableau Server uses the AWS KMS customer master key (CMK) to generate an AWS data key. Tableau Server uses the AWS data key as the root master key for all encrypted extracts. However, even when configured for AWS KMS, the native Java keystore and local KMS are still used for secure storage of secrets on Tableau Server. The AWS KMS is only used to encrypt the root master key for encrypted extracts.
Using AWS to encrypt the master root key provides better security properties by not storing the master key under the same permissions as the extracts.
The key hierarchy when Tableau Server is configured with AWS KMS
Configure AWS KMS for Tableau Server encrypted extracts
To use the AWS customer master key (CMK) to encrypt the root key in the Tableau Server KMS hierarchy, you must configure Tableau Server as described in this section.
Before you begin, verify that you meet the following requirements:
- Tableau Server must be deployed in AWS EC2
- Tableau Server must be configured with a Server Management Add-on license. See About Tableau Server Management Add-on.
- You must have administrative control of a customer master key (CMK) created in AWS Key Management Service
Step 1: Create CMK and set key policy for Tableau Server in AWS
The following procedures are performed in the AWS KMS service. References are included to AWS documentation.
- Create the CMK that you will use for Tableau Server. See the AWS topic, Creating Keys.
- Update the server instance’s IAM role.
Tableau Server needs to be able to authenticate with AWS KMS using the instance’s IAM role. The role needs to have a policy attached to it. The policy should be giving the instance permissions to call the 'GenerateDataKey' and 'Decrypt' actions on the CMK. See IAM Roles for Amazon EC2.
In a multinode deployment of Tableau Server, all nodes of the server must be running under roles that have this policy (or equivalent) attached. You can assign the same role to all nodes in the cluster.
- At a minimum, the CMK must have a key policy where the
Effectis set toAllowthePrinicpal(the IAM role that is attached to the server instances) theAction:GenerateDataKeyandDecrypt. See Using Key Policies in AWS KMS.
Step 2: Collect AWS configuration parameters
You will need the full ARN string from AWS KMS. This string is in the 'General configuration' section of the AWS KMS management pages. The ARN is presented in this format: arn:aws:kms:<region>:<account>:key/<CMK_ID>, for example, arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:867530990073:key/1abc23de-fg45-6hij-7k89-1l0mn1234567.
You will also need to specify the AWS region, which is also included in the ARN string. In the example above, the region is us-west-2. The region is where your KMS instance resides. In the next step, you will need to specify a region as shown in the Region column in the Amazon API Gateway table.
Step 3: Configure Tableau Server for AWS KMS
Run the following command on Tableau Server. This command will restart the server:
tsm security kms set-mode aws --aws-region '<region>' --key-arn 'arn:aws:kms:<region>:<account_number>:key/<CMK_ID>'The
--key-arnoption takes a direct string copy from the ARN in the 'General configuration' section of the AWS KMS management pages.For example, if your AWS KMS instance is running in us-west-2 region, your account number is 867530990073, and your CMK key is 1abc23de-fg45-6hij-7k89-1l0mn1234567, then the command would be as follows:
tsm security kms set-mode aws --aws-region 'us-west-2' --key-arn 'arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:867530990073:key/1abc23de-fg45-6hij-7k89-1l0mn1234567'
Step 4: Enable encryption at rest
See Extract Encryption at Rest.
Step 5: Validate installation
Run the following command:
tsm security kms statusThe following information may be returned:
- The ARN (ID) of the customer master key (CMK)
- The region the CMK is in
- The ID of the root master key (RMK) in use. The RMK is a key that is encrypted by the CMK. Tableau Server decrypts the CMK by making calls to AWS KMS. The RMK is then used to encrypt/decrypt the master extract key (MEK). The RMK can change, but there will be only one at a time.
- KMS stores a collection of master extract keys (MEKs). Each MEK has:
- An ID, for example, 8ddd70df-be67-4dbf-9c35-1f0aa2421521
- Either a “encrypt or decrypt key” or “decrypt-only key” status. If a key is 'encrypt or decrypt', Tableau Server will encrypt new data with it. Otherwise, the key will only be used for decryption
- A creation timestamp, for example, 'Created at: 2019-05-29T23:46:54Z.'
- First transition to encrypt and decrypt: a timestamp indicating when the key became an encrypt or decrypt key.
- Transition to decrypt-only: a timestamp indicating when the key transitioned to decrypt-only.
View logs after you encrypt and decrypt extracts:
Publish extracts to your site and then encrypt them. See Extract Encryption at Rest.
Access the extracts with Tableau Desktop or with Web Authoring on a browser (this will decrypt the extracts for use).
Search the vizqlserver_node log files for the
AwsKmsEncryptionEnvelopeAccessorandAwsKmsEncryptionEnvelopestrings. The default location of the logs are atC:ProgramDataTableauTableau ServerdatatabsvclogsLog entry examples that indicate successful configuration include the following:
- Decrypted the RMK with ID 1abc23de-fg45-6hij-7k89-1l0mn1234567 using the CMK with ARN arn:aws:kms:us-west-2:867530990073:key/1234567d-a6ba-451b-adf6-3179911b760f
- Using RMK with ID 1abc23de-fg45-6hij-7k89-1l0mn1234567 to decrypt KMS store
For publishing and extract refreshes related to KMS, search the backgrounder logs. For more information about logs, see Server Log File Locations.
Troubleshoot configuration
Multi-node misconfiguration
In a multi-node setup for AWS KMS, the tsm security kms status command may report healthy (OK) status, even if another node in the cluster is misconfigured. The KMS status check only reports on the node where the Tableau Server Administration Controller process is running and does not report on the other nodes in the cluster. By default the Tableau Server Administration Controller process runs on the initial node in the cluster.
Call of duty 2 multiplayer key code generator. Therefore, if another node is misconfigured such that Tableau Server is unable to access the AWS CMK, those nodes may report Error states for various services, which will fail to start.
If some services fail to start after you have set KMS to the AWS mode, then run the following command to revert to local mode: tsm security kms set-mode local.
Refresh AWS CMK
Refreshing the AWS CMK is a task that you perform with AWS. By default, the AWS CMK will refresh once a year. See the AWS topic, How Automatic Key Rotation Works. Since the ARN and region do not change, you do not need to update the KMS configuration on Tableau Server for normal CMK refresh scenarios.
After AWS CMK refreshes, you must regenerate the internal RMK and MEKs on Tableau Server. You should also re-encrypt all extracts with the new CMK:
- Run the
tsm security regenerate-internal-tokenscommand to regenerate all internal keys on Tableau Server, including the RMK and MEKs used for extract encryption. - Run
tabcmd reencryptextracts <site-name>to re-encrypt extracts on a given site. Run this command on every site where you are storing encrypted extracts. Depending on the number of encrypted extracts on the site, this operation could consume significant server processing load. Consider running this operation outside of business hours. See Extract Encryption at Rest.
Regenerate RMK and MEK on Tableau Server
To regenerate the root master key and the master encryption keys on Tableau Server, run the tsm security regenerate-internal-tokens command.
Back up and restore with AWS KMS
A server backup can be taken in AWS mode with no additional configurations or procedures. The backup contains encrypted copies of the RMK and MEKs. Decrypting the keys requires access and control of the AWS CMK.
For the restore scenario, the server being restored to can be in either KMS mode, including Local. The only requirement is that the server the backup is being restored to has decrypt access to the CMK the backup itself used.
Upon restore, the MEKs from the backup are imported as decrypt-only keys. The RMK is not migrated over. A new RMK is generated as part of the installation/restore process.
Activate Windows using a Systems Manager Automation document
The AWSSupport-ActivateWindowsWithAmazonLicense Automation document activates an Amazon EC2 Windows instance with a license provided by Amazon. The automation checks the current status of Windows for your instance, and then activates Windows if the status is inactive.
Note: This solution can't be used with Bring Your Own License (BYOL) Windows instances. To use your own license, see Microsoft Licensing on AWS.
1. Open the AWS Systems Manager console. Be sure to select the same Region as the EC2 Windows instance that requires Windows activation.
2. Choose Automation from the navigation pane, and then choose Execute automation.
3. In the search field, enter AWSSupport-ActivateWindowsWithAmazonLicense. Select the Automation document, and then choose Next.
Aws Kms Unable To Generate Data Key In Firefox
4. For Execute automation document, choose Simple execution.
5. For Input parameters, turn on Show interactive instance picker.
6. Choose your EC2 instance.
Note: If you don't see your instance in the list, the instance isn't enabled for Systems Manager. Review the prerequisites for using Systems Manager to manage your Amazon EC2 instances.
If you don't want to enable Systems Manager, or if the instance is not available in Input parameters, turn off Show interactive instance picker. For InstanceID, enter the ID for your impaired instance. For AllowOffline, choose True.
Important: If you set AllowOffline to True, your instance will stop and restart. Data in instance store volumes will be lost. The public IP address changes if you aren’t using an Elastic IP address.
Aws Kms Generate-data-key
7. Choose Execute.
8. To monitor the execution progress, open the Systems Manger console, and then choose Automation from the navigation pane. Choose the running automation, and then review the Executed steps. To view the automation output, expand Outputs.
Activate Windows manually
1. Update EC2Config, or run the EC2Launch initialization script.
For Windows Server 2012 R2 and earlier: Update EC2Config, and then restart the instance.
Aws Kms Keys
For Windows Server 2016 and later: Run the following command to set the correct route to the AWS KMS server: