Generate Ssh Key Mac For Git
You generate an SSH key through Mac OS X by using the Terminal application. Once you upload a valid public SSH key,Gerrit can authenticate you based on this key.
An SSH key consists of a pair of files. One is the private key, which you should never give to anyone. No one will everask you for it and if so, simply ignore them - they are trying to steal it.The other is the public key. When you generate your keys, you will use ssh-keygen to store the keys in a safe locationso you can authenticate with Gerrit.
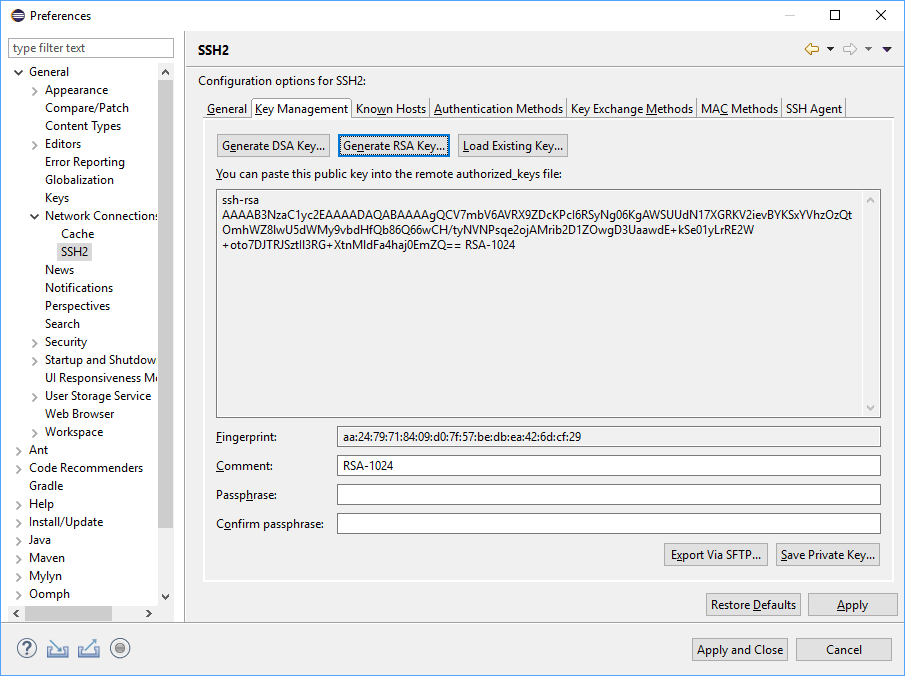
The.pub file is your public key, and the other file is the corresponding private key. If you don’t have these files (or you don’t even have a.ssh directory), you can create them by running a program called ssh-keygen, which is provided with the SSH package on Linux/macOS systems and comes with Git for Windows. Create an SSH key. Follow these steps if you don't already have an SSH key for an account. If you do have an SSH key and you want to generate another key, you'll have to use the terminal because you can't use Sourcetree to create a second key. Creating an SSH key looks something like this: From the Sourcetree menu, select Preferences.
To generate SSH keys in Mac OS X, follow these steps:
Enter the following command in the Terminal window:
This starts the key generation process. When you execute this command, the ssh-keygen utility prompts you to indicate where to store the key.
Press the
ENTERkey to accept the default location. The ssh-keygen utility prompts you for a passphrase.Type in a passphrase. Generate certificate with private key and cabundle. You can also hit the
ENTERkey to accept the default (no passphrase). However, this is not recommended.
On your local machine, use a text editor to create a config file in the /.ssh directory, and then add the following lines to the file, where the value for User is the SSH key ID you copied earlier: Host git-codecommit.amazonaws.com User APKAEIBAERJR2EXAMPLE IdentityFile /.ssh/ codecommitrsa. Aug 08, 2016 Do you hate typing in your username and password for GitHub everytime you make a push? Well that ends today because we are going to learn to generate an SSH key for our computer and to attach it.
Warning
You will need to enter the passphrase a second time to continue.
After you confirm the passphrase, the system generates the key pair and you will see output like this:
Your private key is saved to the id_rsa file in the .ssh subdirectory of your home directory and is used to verifythe public key you use belongs to your Gerrit account.
Warning
Never share your private key with anyone! Ever! We mean it!
Your public key is saved to a file called id_rsa.pub in the .ssh subdirectory of your home directory. You can copyit to your clipboard using the following command:
Now you can head over to Gerrit, go to settings and paste your public key as described here.
Gerrit is using the special port 29418 instead of the default SSH port 22 which has to be configured accordingly. This can be done in your local ~/.ssh/config file which would contain the following sections then:
Testing your connection:
-->Azure Repos Azure DevOps Server 2019 TFS 2018 TFS 2017 TFS 2015 Update 3
Choose a method to securely access the code in Azure Repos, Azure DevOps Server 2019, or Team Foundation Server (TFS) Git repositories.Use these credentials with Git at a command prompt. These credentials also work with any Git client that supports HTTPS or SSH authentication.Limit the scope of access and revoke these credentials when they're no longer needed.
Important
Generate Ssh Key Mac Git
Azure DevOps no longer supports Alternate Credentials authentication since the beginning of March 2, 2020. If you're still using Alternate Credentials, then they won't work anymore. You have to switch to a more secure authentication method, to mitigate this breaking change impacting your DevOps workflows. Learn more.
Azure DevOps Server was formerly named Visual Studio Team Foundation Server.
Tip
Using Visual Studio? Team Explorer handles authentication with Azure Repos for you.
Authentication comparison
| Authentication Type | When to use | Secure? | Ease of setup | Additional tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personal access tokens | You need an easy to configure credential or need configurable access controls | Very secure (when using HTTPS) | Easy | Optional (Git credential managers) |
| SSH | You already have SSH keys set up, or are on macOS or Linux | Very secure | Intermediate | Windows users will need the SSH tools included with Git for Windows |
| Alternate credentials | You can't use personal access tokens or SSH | Least secure | Easy | See important information about alternate credentials |
Personal access tokens
Personal access tokens (PATs) give you access to Azure DevOps and Team Foundation Server (TFS), without using your username and password directly.These tokens have an expiration date from when they're created. You can restrict the scope of the data they can access.Use PATs to authenticate if you don't already have SSH keys set up on your system or if you need to restrict the permissions that are granted by the credential.
Generate Ssh Key Mac For Git Download
Use Git Credential Manager to generate tokens
Git credential managers is an optional tool that makes it easy to create PATs when you're working with Azure Repos.Sign in to the web portal, generate a token, and then use the token as your password when you're connecting to Azure Repos.
PATs are generated on demand when you have the credential manager installed.The credential manager creates the token in Azure DevOps and saves it locally for use with the Git command line or other client.
Note
Current versions of Git for Windows include the Git credential manager as an optional feature during installation.
SSH key authentication
Key authentication with SSH works through a public and private key pair that you create on your computer.You associate the public key with your username from the web. Azure DevOps will encrypt the data sent to you with that key when you work with Git.You decrypt the data on your computer with the private key, which is never shared or sent over the network.
SSH is a great option if you've already got it set up on your system—just add a public key to Azure DevOps and clone your repos using SSH.If you don't have SSH set up on your computer, you should use PATs and HTTPS instead - it's secure and easier to set up.
Learn more about setting up SSH with Azure DevOps
Alternate credentials
Create an alternate user name and password to access your Git repository using alternate credentials.Unlike PATs, this login doesn't expire and can't be scoped to limit access to your Azure DevOps Services data.Use alternate credentials as a last resort when you can't use PATs or SSH keys.